In OEM and ODM product design, the logo is an important part of the brand image and a detail of the product. It can convey the company’s cultural concept and brand characteristics to a certain extent. A good product LOGO design should have attractive information, improve the grade of the product, and help increase product sales.
Then this article will introduce the common logo processing techniques in product design, which will help you decide what kind of logo processing process is most appropriate when ordering products from suppliers.
Screen Printing:
What is Screen Printing?
Screen printing is one of the most common surface treatment process, is to screen as the plate base, and through the photographic plate making method, made with graphic printing effect, the process has been very mature. The principle and process of screen printing is very simple, that is, the use of graphic part of the mesh through the ink, non-graphic part of the mesh opaque ink basic principles of printing. Printing in one end of the screen printing plate poured into the ink, with a scraping scraper in the screen printing plate on the ink parts of a certain pressure, while moving towards the other end of the screen printing plate. The ink is squeezed by the squeegee from the mesh of the graphic portion of the screen to the substrate as it moves.
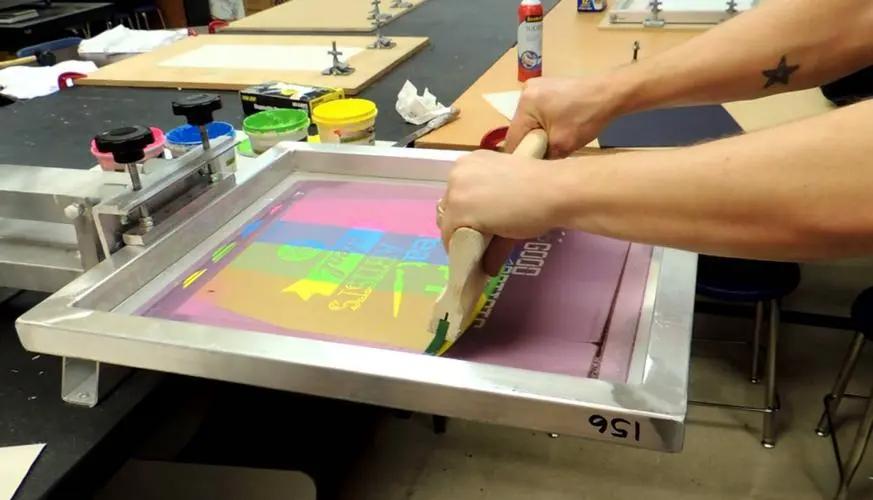

Best for:
Flat surfaces
Pros:
– Durability:Screen printing produces vibrant colors that can withstand repeated washes and wear, making it ideal for apparel.
– Cost-effective for bulk: The setup costs can be high, but once the screens are created, producing large quantities is cost-efficient.
– Versatility: It works well on a variety of materials like fabric, plastic, and paper.
Cons:
– Setup costs: Creating the screens is labor-intensive and costly, especially if your logo has multiple colors.
– Not great for detailed designs: Fine details can get lost in the process, and color gradients are challenging to achieve.
Cost:
– Setup Fee: $20 – $50 per color for creating screens.
– Per Unit Cost: $1 – $5 per item, depending on the number of colors and the complexity of the design.
– Bulk Discounts: The more you produce, the cheaper it gets, often reducing the per-unit cost by 50% or more for large orders.
Heat Transfer Printing:
What is Heat Transfer Printing?
Heat transfer printing uses heat to transfer a printed image from a special paper onto the product. This method is popular for custom, short-run orders and allows for vibrant, full-color designs.
Best for:
– Custom T-shirts
– Sportswear
– Promotional products like mouse pads and keychains
Pros:
– Full-color printing: Unlike screen printing, heat transfer allows for complex, full-color images with gradients and fine details.
– No setup fees: This method doesn’t require screens or plates, making it cost-effective for small batches.
– Versatility: It can be used on a wide range of materials, including polyester, cotton, and even ceramic.
Cons:
– Less durable: The prints may crack or fade over time, especially after multiple washes.
– Not ideal for bulk orders: While good for small runs, it’s less cost-effective for large quantities compared to screen printing.
Cost:
– Setup Fee: Usually minimal or none, since it doesn’t require screens.
– Per Unit Cost:$2 – $10 per item, depending on size and complexity.
– Bulk Discounts: Not as significant as other methods, with savings typically around 10-20%.
Pad Printing:
What is Pad Printing?
Pad printing is the current LOGO processing process is more widely used, belongs to one of the special printing methods, able to print text, graphics and images on the surface of irregular shaped objects, commonly known as universal printing.
Specifically, pad printing is the need to print the pattern first with film etching made of steel (or copper, thermoplastic) intaglio, and then the use of silicone rubber material made of curved pad printing head, the intaglio on the ink dipped into the surface of the pad printing head, and then to the need for the surface of the object to be able to print out the text, patterns, etc. Pressing the surface of the object.
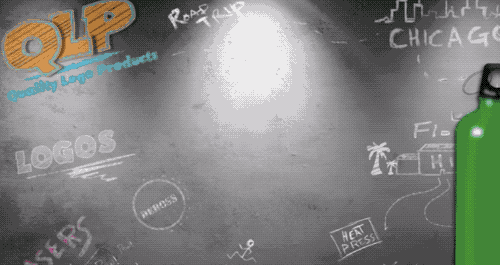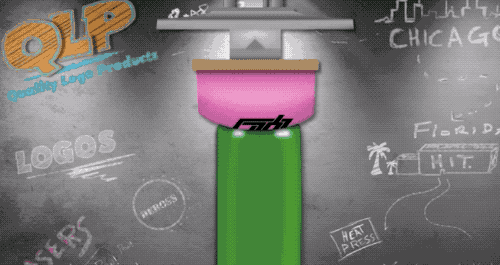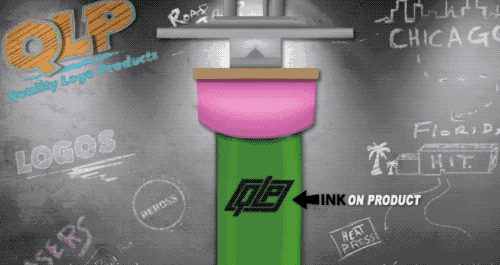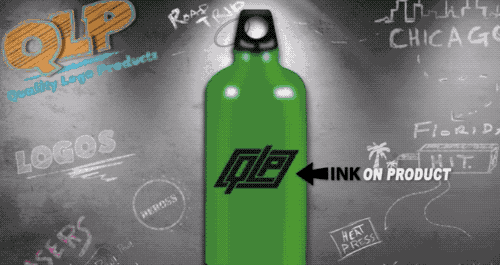
Best for:
– Promotional items like pens, mugs, and keychains
– Electronics and gadgets
– Products with uneven surfaces
Pros:
– Versatile on 3D objects: Pad printing works well on curved and irregular surfaces where other methods might struggle.
– Precise and detailed: It’s excellent for small logos and fine details.
– Good for bulk production: Once the pad is created, it’s cost-efficient for large quantities.
Cons:
– Limited color range: Typically limited to one or two colors per print, which can make complex logos difficult to reproduce.
– Setup costs: Initial setup can be expensive due to the creation of the pad and other tools.
Cost:
– Setup Fee: $20 – $50 depending on the complexity and number of colors.
-Per Unit Cost:$0.10 – $2 per item, with significant savings for large orders.
-Bulk Discounts: Substantial, often reducing costs by 50% or more for large volumes.
Laser Engraving:
What is laser engraving?
Laser engraving and laser engraving are the same process, which is a surface treatment process using CNC plus laser. The principle is that the laser can achieve the engraving effect by controlling the path of the laser on the surface of the material when the surface is irradiated, and the required graphic mark can be formed. This is a popular choice for metal, glass and wood products that require stylish and low-key logos.

Best for:
– Metal products,
– Wooden items,
– Plastic products, etc.
Advantages:
-High precision:Laser engraving is very precise and is ideal for making detailed logos and complex designs.
-Permanent:Logos will not fade, chip or fall off, ensuring long-term durability.
Disadvantages:
Limited colors:Laser engraving does not usually add color to the logo, so it is best suited for designs in monochrome format.
Cost:
-Installation fee: Depends on the complexity of the design.
-Cost per unit:$1-5 per piece, depending on materials and complexity of design.
-Volume discounts:Discounts can be significant, with costs reduced by 20-50% for large orders.
Mold engraving:
What is Mold engraving?
Mold engraving is a production method that engraves the logo on the mold surface in advance, and then uses the mold to transfer the logo to the material.

Best for:
– Custom products
Pros:
The advantage is that it is formed in one step, no secondary processing is required, and it is not easy to wear.
Cons:
-Too expensive;
-Difficult to change.
Cost:
-Setup fee: The mold fee will be determined based on the specific product and the complexity of the LOGO, usually more than $1,000;
-Cost per unit: $1-5 per piece, depending on the size of the order quantity.
-Bulk discount: Smaller discount than other methods, large order discounts are usually about 10-30%.
UV Printing:
What is UV Printing?
UV printing is a digital printing technology that uses ultraviolet (UV) light to cure or dry the ink as it’s printed. This method produces high-quality, vibrant prints with excellent durability, and it can be used on a wide variety of materials, including plastic, metal, glass, and wood.

Best for:
– Promotional items like pens, USB drives, and phone cases
– Signage and displays
– Products with hard surfaces like glass and metal
Pros:
-High-quality prints:UV printing produces sharp, detailed images with vibrant colors.
-Durability:The UV-cured ink is resistant to fading, scratches, and other wear and tear.
-Versatility:It works well on a wide range of materials, including curved and uneven surfaces.
Cons:
-Higher cost for small runs:The technology is relatively expensive, making it less cost-effective for small orders.
-Surface limitations:While versatile, UV printing may not adhere well to certain surfaces without proper preparation.
Cost:
-Setup Fee:Typically none, but some suppliers may charge a small fee depending on the complexity of the job.
-Per Unit Cost:$2 – $20 per item, depending on the material, size, and complexity of the design.
-Bulk Discounts:Savings can be significant, often reducing costs by 20-40% for larger orders.
Hot Stamping:
What is Hot Stamping?
Foil stamping with silver is a common logo making process. Hot stamping is the use of the principle of thermal pressure transfer, the metal printing plate is heated, the foil is applied, and the gold text or pattern is embossed on the printed materials. Because the main material used in hot stamping is electrified aluminum foil, so hot stamping is also called electrified aluminum stamping. And hot stamping silver and hot stamping gold is not much difference, just choose a different material, from the appearance, hot stamping silver present silver luster; hot stamping gold present gold luster.

Best for:
– Luxury packaging and labels
– Stationery items like business cards and invitations
– Leather goods
Pros:
-Luxurious finish:Hot stamping adds a metallic or shiny finish that can elevate the perceived value of the product.
-Durability:The stamped design is resistant to wear and fading, making it long-lasting.
-No ink required:This method doesn’t rely on ink, so there’s no risk of smudging or running.
Cons:
-Higher setup costs:The dies required for hot stamping are expensive to produce, making it costly for short runs.
-Limited color options:Typically limited to metallic and pigmented foils, which might not suit every design.
Cost:
-Setup Fee:$50 – $200 for die creation, depending on the complexity of the design.
-Per Unit Cost:$0.10 – $5 per item, depending on the material and design.
-Bulk Discounts:Significant discounts for large orders, often reducing costs by 30-50%.
Labeling:
What is Labeling ?
The process of making the logo in advance and then attaching it to the product.

Best for:
Most products.
Pros:
The advantage is that it can be pasted on different surfaces. Better texture and better design.
Cons:
– High material cost
– High labor cost
Cost:
-Setup Fee:Typically none, but design costs can be significant depending on complexity.
-Per Unit Cost:$1 – $5 per item, depending on material, size, and complexity.
-Bulk Discounts:Less significant compared to traditional methods, with savings typically around 10-20%.
Translucent surface + backlight:
This is a design that incorporates electricity and light. The surface of the product is made of translucent plastic or rubber, and then sprayed to make the whole body opaque, and then the shape of the LOGO is scraped out, and an LED light is added on the back.

Best for:
Most products.
Advantages:
Brings an atmospheric effect, making the product more distinctive.
Disadvantages:
– Specific materials are required
– Complex process
Cost:
-Installation fee:Usually none.
-Cost per unit:$1 – $5 per piece, depending on material, size and complexity.
-Bulk discounts:Smaller discounts compared to traditional methods, usually around 10-20% savings.
Comparing the Costs:
Understanding the costs associated with different logo processing methods can be tricky since they vary based on factors like material, design complexity, and order size. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Method | Setup Fee | Per Unit Cost | Best For | Bulk Discount |
| Screen Printing | $20 – $50 per color | $0.1 – $2 | flat surfaces | 30-50% |
| Heat Transfer | None | $2 – $10 | Custom apparel, small runs | 10-20% |
| Pad Printing | $20 – $50 | $0.10 – $2 | 3D objects | 50%+ |
| Laser Engraving | None | $1 – $5 | Metal, glass, Plastic | 20-50% |
| Mold engraving | $1000 | $0.50 – $5 | Custom products | 30-50% |
| UV Printing | None | $2 – $20 | most items | 20-40% |
| Hot Stamping | $50 – $200 | $0.10 – $5 | Luxury items | 30-50% |
| Labeling | None | $1 – $5 | Most items | 10-20% |
| Translucent surface + backlight | None | $1 – $5 | Custom items | 10-20% |
FAQs:
1. Which logo treatment is the most cost-effective for large orders?
– Screen printing is usually the most cost-effective method for large orders.
2. Which method has the highest durability? **
– Laser engraving, die engraving will be the best choice.
3. Can I use multiple logo treatments on a single product? **
– Yes, some products can be highlighted with a combination of multiple treatments.
4. How do I choose the best treatment for my product?
– Consider the material of the product, the complexity of the logo. Secondly, you also need to consider the product’s positioning and budget.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right logo treatment depends on a variety of factors, including the material of your product, the complexity of your design, and your budget. For example, screen printing is ideal for bulk orders, while laser engraving provides a refined finish for metal products. Other product treatments are often chosen based on the product’s positioning and features.
When planning your branding strategy, weigh the costs and benefits of each approach. Consider not only the initial cost, but also the potential savings from bulk discounts and the quality of the finished product.
